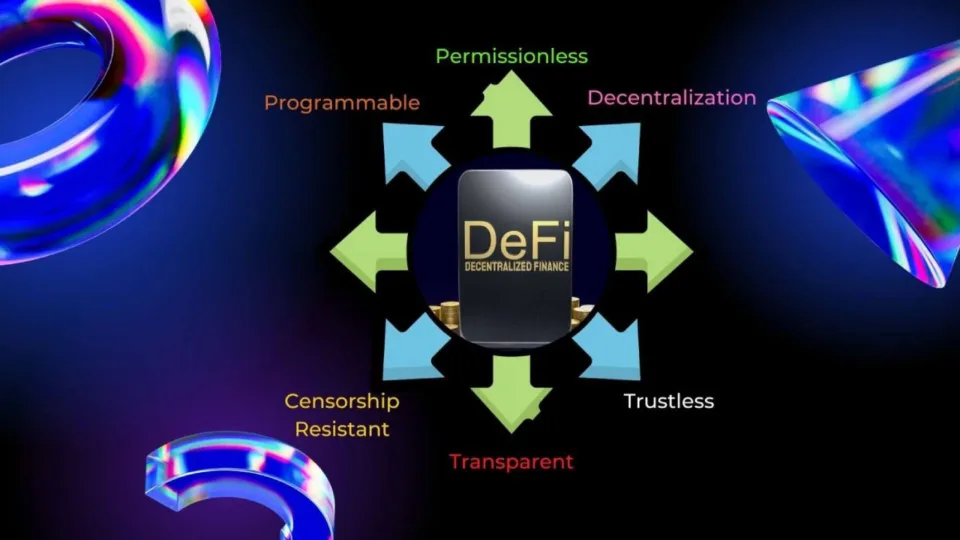
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Definition
DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance, and as the name suggests it encompasses the idea of finance not being held on a single server, but on many different ones.
DeFi’s primary motivation is to eliminate third-party intermediaries in finance to solve trust issues lingering around the traditional financial sector. It also intends to make anyone and everyone from whichever part of the world eligible for banking through the internet. Over 1.5 billion people around the world lack access to essential financial services. DeFi participants can partake in most functions found in a typical bank, such as saving, investing, borrowing, and even lending. You can also buy insurance, trade contracts for difference (CFDs), and much more. And it’s faster as you don’t have to go through intermediaries. DeFi transactions are of a peer-to-peer nature.
Understanding Decentralized Finance (DeFi) & Centralized Finance(CeFi)
Centralized Finance (CeFi)
Centralized finance is the opposite of DeFi. Both offer services like savings, lending, and investment, except that CeFi does so through a third party.
Traditional banks are the best example. They control every aspect of their clients’ lives, from receiving their money to sending it. They decide when you can access your funds and even implement government regulations on your money. Customers pay a fee for each service rendered to them. There is no way to bypass these middlemen as long as you are using their services.
Regulatory authorities like FED and SEC in the US enforce laws that govern how money moves in centralized finance.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized finance, on the other hand, promotes freedom and democracy in the way transactions are done. It takes away power from monopolies and hands it over to the people. The commoner is exploited in traditional finance. Today if you have money in your savings account, you’re probably earning an interest of, say, 0.5%. You may not know that the bank uses your money to do business. It lends it, to other customers, at a high rate, like 3%, and only pays 0.5%, which is only about 15% of the profits they made with your money. DeFi gives you a platform where you can lend to borrowers directly and earn the entire 3% profit.
Benefits of DeFi
 The benefits are numerous, and they include the following:
The benefits are numerous, and they include the following:
Permissionless and Inclusive
It is permissionless, thus, anyone with an internet connection can access the associated products and services without the need for a middleman or intermediary. This is a significant departure from the traditional finance system, which is highly regulated and requires users to go through a rigorous process of identity verification and authorization before they can access financial services.
The permissionless nature of this technology makes it more inclusive, as it allows individuals who may not have access to traditional banking services to access financial products.
Transactions are Processed Instantly
The transactions are processed instantly, making it a faster and more efficient way of conducting financial transactions compared to traditional finance. The transactions are executed on blockchain networks that operate 24/7 without any downtime, and do not require intermediaries such as banks or financial institutions to validate and process them.
Moreover, the decentralized nature eliminates the need for time-consuming manual processes, which are often required in centralized financial systems to validate transactions. Thus, transactions can be settled almost immediately, and funds can be transferred directly between the transacting parties without any delay.
Transactions are Transparent
The transactions are transparent because they are executed on a blockchain, which is a public and immutable ledger. Thus, all transaction data is visible to everyone with access to the blockchain, making it possible for anyone to track and verify the authenticity of transactions.
Users can view the history of any transaction, which includes information such as the transaction amount, sender and receiver addresses, and timestamp. This enables users to verify the integrity of transactions and provides a level of security that is not available in traditional finance.
The transparency also reduces the risk of fraud and corruption, as all transaction data is publicly visible and tamper-proof. This makes it difficult for bad actors to manipulate transaction data, commit fraud, or engage in other illegal activities.
Users have Control Over their Assets
The users have full control over their assets. Thus, users can manage their assets without the need for intermediaries. This is made possible through the use of blockchain technology and smart contracts, which allow for the creation of self-executing financial contracts that automatically execute the terms of the contract when certain conditions are met.
It helps users to store, transfer, and manage their assets directly, without the need for intermediaries like banks or other financial institutions. This puts the control of the assets back in the hands of the users, and allows them to manage their finances more securely and efficiently.
Smart Contracts are Highly Programmable
Smart contracts are highly programmable, thus, they can be customized to suit the needs of specific users or applications. This flexibility allows developers to create a wide range of financial products and services that operate without intermediaries, making it a highly versatile financial ecosystem.
Smart contracts can be used to create a variety of products and services, including decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, insurance products, and more. These products and services operate on the blockchain, providing greater transparency, security, and efficiency.
Data is Tamper Proof, Secure, and Auditable
It is built on blockchain technology, which allows for the creation of a transparent and tamper-proof record of all financial transactions. This ensures that all data in the ecosystem is secure and cannot be altered or manipulated by any one party. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology ensures there is no single point of failure or control, making it a more secure alternative to centralized systems.
Furthermore, the use of smart contracts provides an additional layer of security. Smart contracts are self-executing programs that are coded to execute specific functions when certain conditions are met. Once the conditions are met, the contract automatically executes the programmed function without the need for human intervention. This removes the risk of human error and ensures that all transactions are carried out as programmed. The transparency and security of data also makes it auditable, implying that any user can view and verify the details of a transaction that occurs on the blockchain.
Many Protocols are Open Source
Open source refers to the concept of making software code publicly accessible for anyone to use, modify, and distribute. Many protocols are open source, which means that anyone can access the code and contribute to its development. This promotes collaboration and innovation within the Decentralized Finance community, as developers can work together to improve the functionality of the products and services.
Risks and Challenges
While Decentralized Finance is a promising space, it comes with its own set of risks and challenges. Below, we explore some of the potential risks and challenges associated with it.
 Smart-Contract Risk
Smart-Contract Risk
One of the most significant risks is smart-contract risk. Smart contracts are self-executing computer programs that govern the behavior of a blockchain network.
However, the code that powers smart contracts is not perfect and may contain errors or vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit to steal funds. In the past, several platforms have fallen victim to smart-contract attacks, resulting in significant financial losses for users.
One example of a smart-contract attack is the “DAO hack” that occurred in 2016. The DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) was a venture capital fund built on the Ethereum blockchain that allowed investors to vote on which projects to fund. However, a flaw in the DAO’s smart contract allowed a hacker to siphon off a significant amount of the fund’s assets, resulting in a loss of over $50 million worth of Ether.
Oracle Risk
Decentralized Finance applications rely on oracles to access data from external sources, such as market prices, to execute smart contracts. Oracles are third-party services that supply external data to a blockchain network. Chainlink, Band Protocol, Augur, MakerDAO, Tellor, API3, and DIA are some of the well-known reputed oracles.
However, the accuracy and reliability of these external data sources is not always guaranteed, and they may be susceptible to manipulation or hacking. Malicious actors can compromise oracles and manipulate the data that smart contracts rely on, leading to inaccurate or faulty execution of the contracts.
One such example is the “flash loan attack” on the bZx decentralized finance platform in February 2020. The attacker manipulated the price data from an oracle, causing the platform to provide a loan worth more than the collateral. This resulted in the attacker receiving a profit of approximately $350,000.
Scaling Risk
It has grown rapidly in recent years, but the underlying blockchain technology still faces scalability challenges. Blockchain networks have limited processing capacity, and as the number of users and transactions increase, the networks can become congested and slow down.
This can result in higher transaction fees and longer confirmation times, reducing the user experience and making the applications less accessible to the masses.
As an example, during the peak of the 2021 crypto bull run, the transaction fees on the Ethereum network (which is used by many applications) rose to unprecedented levels due to high demand and network congestion. At one point in May 2021, the average transaction fee on the Ethereum network was around $70, with some transactions costing as much as $500 or more.
At the same time, the confirmation times for Ethereum transactions also increased significantly, with some transactions taking several hours or even days to be confirmed. This can create frustration for users who may be trying to take advantage of time-sensitive opportunities, such as trading or investing in projects.
Higher transaction fees and longer confirmation times can also make such applications less accessible to users with smaller budgets who may be priced out of the market. This underscores the need for ongoing efforts to improve the scalability and performance of blockchain networks to ensure that it remains accessible and affordable for everyone.
Custody Risk
Such apps provide users full control over their assets, and are responsible for safeguarding their private keys. However, this responsibility can be daunting for new users who are not familiar with managing crypto assets.
Storing crypto assets safely requires users to take appropriate measures, such as using secure wallets, like hardware wallets, and following best practices for key management. Failure to do so can lead to loss or theft of funds.
Regulatory Risk
![]() The regulatory environment is still evolving, and there is uncertainty around how the platforms and protocols will be treated by regulators. While Decentralized Finance is designed to be decentralized and permissionless, regulatory bodies may seek to impose restrictions or regulations on the space.
The regulatory environment is still evolving, and there is uncertainty around how the platforms and protocols will be treated by regulators. While Decentralized Finance is designed to be decentralized and permissionless, regulatory bodies may seek to impose restrictions or regulations on the space.
One example of a regulatory restriction is China’s ban on all cryptocurrency trading and mining activities, including Decentralized Finance platforms, which was announced in 2021. The Chinese government’s decision was aimed at cracking down on speculative trading and addressing concerns around energy consumption, which led to a significant drop in the value of cryptocurrencies.
In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has taken a more cautious approach to crypto regulations, as there have been calls for increased oversight of the space. In 2021, the SEC took enforcement action against several platforms, including Uniswap, for offering unregistered securities. The SEC’s actions have created uncertainty for developers and users, who may be unsure of how to comply with regulations while still preserving the decentralized nature of the apps.
In Europe, the regulatory landscape is also evolving. The European Union has proposed new regulations aimed at increasing transparency and reducing risks associated with cryptocurrency transactions. The proposed regulations would require crypto exchanges and other service providers to follow anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing rules.
These are just a few examples of the regulatory risks. As the regulatory environment continues to evolve, developers and users will need to stay informed about the latest regulations and work to ensure compliance while still maintaining the decentralized and permissionless nature of the ecosystem.
Not an Even Playing Field
The ecosystem is not an even playing field, with some users and protocols having more power and influence than others. Large investors and liquidity providers can have a disproportionate impact on the market, potentially making it difficult for smaller players to compete.
An example of this could be seen in the recent “rug pull” incident involving one such platform, Meerkat Finance, which saw the protocol’s developers abscond with $31 million of user funds. According to reports, the majority of the funds were owned by just a handful of large investors who were able to gain outsized influence over the platform. This incident highlights the potential risk for smaller investors in the ecosystem, where power and influence can be concentrated among a select few. Additionally, the concentration of funds among a small group of investors can also impact the liquidity and stability of the market, as sudden movements by these large investors can have a significant impact on the market as a whole.
Difficult to Collect Taxes
The decentralized nature makes it difficult for regulators to monitor and collect taxes on transactions. This poses a challenge for governments seeking to tax DeFi activities, making it an area of regulatory uncertainty.
Governance Issues Plague the Sector
Projects in this sector often involve complex governance structures, with various stakeholders and participants having a say in the direction and management of the project. Governance issues, such as disputes over decision-making, can create uncertainty and potentially harm the project’s reputation.
Traditional vs. Decentralized Finance: How Different is DeFi From Other Banking Products?
Management
Employees manage normal banking products in an institutional setup. These are the people responsible for ensuring that transactions are fulfilled as they should. DeFi is an algo-managed environment in conjunction with smart contracts. Once a smart contract is deployed, the DeFi app handles the entire transaction according to the rules of the agreement without requiring human intervention.
Trustless
Transparency is one of the founding principles of blockchain technology. It’s, in fact, among the vital differences between DeFi products and traditional banking products. Blockchain transactions are available to everyone at any time, something that creates trust among the community. In addition, there are no privacy concerns since transactions happen in a pseudonymous fashion.
Accessibility
Traditional banks are geographically limited. Even for those with online banking, clients are still required to visit the banking hall for certain transactions. DeFi is 100% online and can be accessed from any part of the world.
Permissionless
Present-day bank accounts have specific requirements that may limit people of certain categories from using them. DeFi is permissionless. There are no KYC requirements or credit history audits. It’s open to everyone. Since there are no gatekeepers, anyone is free to build new DeFi apps or use existing ones. All this is enabled by the power of smart contracts.
Quick Innovation
The open-source nature of DeFi makes it programmable. Since it’s trustless, any programmer can add new ideas. Of course, some never see the light, but the ecosystem is always filled with new products from all angles of creativity. That is why DeFi is growing at a tremendous speed.
CeFi Vs DeFi
| CeFi | DeFi | |
|---|---|---|
| Funds Custody | The exchange has custody | User has complete custody |
| Security | Exchange can be hacked | No funds in the exchange to hack |
| Customer Service | Easily available | Hardly offered |
| Costs | Higher fees and commissions | Low fees |
| Access | KYC verification required | Permissionless |
| Anonymity | Very little | High anonymity |
The Most Important Defi Terms Explained
- AMM: Automated Market Makers (AMMs) facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers via smart contracts. So they eliminate the need for third parties or direct meetings between transacting parties.
- Bitcoin Maximalist: Also called “Bitcoin Maxis.” They are notorious supporters of Bitcoin who believe it’s the Bitcoin is the only true crypto, and the rest are pump and dump schemes.
- Black Swan: Black swans refer to catastrophic occurrences in DeFi. These are events that are normally unseen yet leave a widespread effect across the entire market.
- Censorship Resistant: These are protocols whose transactions can’t be invalidated or interfered with. DeFi is censorship resistant because no one can stop its transactions.
- DAO: Members create Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) to automate decision-making through a governance token.
- Deflationary Token: Tokens are “deflationary” if their supply is constantly reduced from the market to cause scarcity and raise prices.
- dApps: Decentralized applications (dApps) are digital apps that run on the decentralized blockchain.
- Derivatives: Derivatives are securities whose value reflects the price of an underlying asset or group of assets. Therefore they don’t have an intrinsic value.
- ERC-20: This is an Ethereum network standard for running smart contracts. It carries the rules that govern all Ethereum tokens.
- Flash Loan: Flash Loans are a type of uncollateralized or unsecured loans accessible through DeFi platforms. They are governed by smart contracts and are paid back within seconds.
- Gas: Gas is the cost of performing transactions on a network. It’s normally determined by the miners according to the demand and supply of computing resources. Gas fees are higher when the network is congested and vice-versa.
- Governance Tokens: These tokens allow DAO members to vote. The weight of a vote is determined by the number of tokens held by the voter.
- Liquidity: Liquidity is the availability of liquid assets in DeFi.
- Liquidity Pools: Liquidity pools are made up of pooled assets locked in by smart contracts and are meant to facilitate trading.
- Off-Chain & On-chain: Off-chain transactions occur “off” the blockchain network. They are mostly free. While on-chain transactions take place take place on the Ethereum network, hence subject to gas fees.
- Web 3.0: This is an internet built on the blockchain and gives users autonomy over information. It’s decentralized and benefits both builders and users.
- Yield Farming: Refers to the act of investing tokens in DeFi to earn interest.
- Decentralized Exchange (DEX): a platform that enables users to trade cryptocurrencies without the need for an intermediary.
- Money Legos: the ability to stack, combine, and integrate different protocols to create new and more complex financial products. This idea is possible due to the composability of such protocols, which can easily interact and connect with each other.
- Open-Source: software that is publicly available for anyone to use, modify, and distribute. Many platforms are open-source, allowing developers to access the code and make improvements to it.
- Oracle: service that provides data to smart contracts. Oracles are used in such platforms to ensure that the smart contracts have accurate and up-to-date information about the value of assets and other important data.
- Over-Collateralization: concept where a borrower provides more collateral than the value of the loan. This ensures that lenders are protected in case the value of the collateral falls. For example, if a borrower wants to take out a loan of $10,000, they may be required to provide $15,000 worth of collateral.
- Permissionless: a platform where anyone can participate without the need for prior authorization or documentation. This makes the platform accessible to people who are excluded from traditional financial systems due to their location, status, or other reasons.
- Smart Contracts: self-executing contracts that are programmed to execute when certain conditions are met. Smart contracts are used in DeFi platforms to automate financial transactions, making them more secure and transparent.
- Tokenization: the process of converting an asset, whether tangible or intangible, into a digital token on a blockchain. This allows the asset to be easily traded and transferred within the blockchain ecosystem.
- Total Value Locked (TVL): metric used to measure the amount of assets currently locked in a protocol. It is calculated by taking the sum of all assets, including cryptocurrencies and stablecoins, that have been deposited in a particular protocol.
- APY and APR: Annual Percentage Yield (APY) and Annual Percentage Rate (APR) are both measures used to calculate the return on investment. APY takes into account the effect of compounding interest, while APR does not. APY is generally a more accurate measure of the true return on investment because it considers the effects of compounding over time.

How Does DeFi Work?
DeFi is enabled by the blockchain network and crypto. In traditional finance, there’s a physical ledger book or computer ledger software that banks use to record transactions. This is called a private ledger. It can only be accessed by the institution in charge.
DeFi has a ledger too. All transactions are recorded in a coded format. The difference with your bank is that DeFi uses a public ledger. Anyone can check the ledger and view all the recorded transactions. The addresses involved, which are like bank accounts, are also visible. However, personal information such as the owners of the address is kept private. DeFi ledgers are also said to be distributed, meaning that anyone using the platform has the same copy of records in encrypted codes. It’s theoretically impossible to alter a transaction that has already been recorded. That’s why it’s said that blockchain activities are immutable. Immutability guarantees security and increases trust between users and the system.
Smart Contracts
DeFi takes advantage of smart contracts to offer all traditional banking services without third parties and central governing authorities. It hence makes it possible for anyone to access services such as banking, money transfer, and saving from any part of the world. All that’s needed is a connection to the internet.
Smart contracts are also eliminating banking instruments such as documentary letters of credit and the costs involved. You can perform a complex sales transaction such as the purchase of real estate automatically by simply setting up or following a smart contract. The smart contract executor protocols will transfer the titles of ownership and money when the required conditions are fulfilled. DeFi is not yet complete, even though its fruits are already being harvested. It’s a continuous work in progress. Keep in mind that it’s not owned by anyone, just like the internet.
What Can You Do With DeFi?
You can engage in DeFi via blockchain software called dApps (decentralized applications), or simply called DeFi projects. Most dApps / DeFi projects currently run on the Ethereum blockchain. Here are some of the ways people are participating in DeFi
- Lending: Instead of holding your crypto tokens in your wallet with no use, you can lend them out to the network. In return, you get rewards in the form of more crypto (interest). Unlike traditional banking, DeFi rewards can start streaming in almost as soon as you lend your crypto.
- Borrow: Since there is a lending function, borrowing is also part of DeFi. You can obtain a loan instantly without following lengthy application processes. DeFi offers extremely short-period unsecured loans called flash loans to longer-term collateral-based loans. Your credit history is not important.
- Trading: DeFi’s automated market maker system allows you to engage in peer-to-peer trading of financial assets. You can also take part in derivative trading and earn quick leveraged returns.
- Savings: You’ll come across attractive saving plans in the DeFi environment. Here you can put your crypto in a saving dApp and earn better interest than what your bank gives you.
- Gambling: Gamblers are never left out of any new technology. Casinos and other gambling operators have already joined DeFi and are known as DeFi Casinos. This has promoted the development of a decentralized betting ecosystem like LunaFi, where anyone can invest and become the house.
What Are Yield Farms?
Yield farming is an umbrella word for different ways of earning interest from your crypto. It can be compared to how you can earn from saving in the bank or even taking an insurance investment policy. Most of it requires you to lock up your crypto for a while and in the end, take away rewards in the form of more crypto. In Defi, investors put their money/tokens/coins in dApps such as crypto wallets and decentralized exchanges to earn interest. Yield farming is a function of smart contracts.
There are several ways to participate in yield farms with your digital assets. Staking is one of the most common ways. Proof-of-stake blockchain networks like Solana and Polkadot will reward you for verifying transactions on the network. You may also invest in a lending protocol app like Compound and earn dynamic interest rates.
Lastly, you can become a liquidity provider for decentralized exchanges like Uniswap. This involves investing a pair of crypto tokens in equal measure to facilitate digital assets swaps in decentralized exchanges. By doing so, you’ll share in the platform’s profits for fees collected from investors exchanging one currency for another.
Degen vs. Stable Yield Farming
There are always two types of investors; aggressive high risk, and low risk, also called conservative type investors. Degen and stable yield farming represent these two types of investors, respectively. Let’s dig deeper.
Degen Yield Farming
Degen yield farms take outrageous risks far from normal risk protocols and target extremely high returns, therefore it is also considered as DeFi gambling. While the chances of catastrophic outcomes are high, investors can take home double or even triple their returns when things go right. Unfortunately, most yield farming tokens have weak use cases and are simply backed by investor speculations and hype. They hardly have proper documents or undergo code audits. These are zero-sum games where you either win big or lose big. Outcomes can be determined starting from a few hours, days to weeks. Successful degen farm investors get in early and exist quickly too.
Stable Yield Farming
On the other hand, stable yield farming involves taking low risks and targeting relatively low to moderate returns. They are usually backed by reputable teams and have a proper project behind them. The annual percentage returns (APRs/APYs) are never anywhere close to 100%
What is the total value locked or TVL?
TVL is a figure indicating the amount of money or assets staked in a particular DeFi protocol at a given time. It’s a key indicator of the overall health of yielding markets in decentralized finance. So when you want to find the dollar value of crypto locked in any DeFi project, you look for the TVL. Any smart investor must know where money is moving in the current highly saturated crypto market. You don’t want to invest in every other hyped-up project, but where you’ll make money. The thing is, crypto trading is a game of demand and supply. You’re only sure to rake in huge profits when you stake your money in a protocol attracting many other investors.
How You Can Start Using DeFi – Step by Step Guide
Step 1 — Decide your initial Investment
The best way to get started is to get involved. After reading and doing tons of research, you still can’t get better at it if you’re not a participant. Beginners should start with a small amount that they are willing to risk. Remember, profits and losses are part of business, so don’t put in your entire savings. You may also not want to start with borrowed capital unless it’s money that can’t strain you if it fails to pay off.
Step 2 — Converting Fiat to Crypto/USD (Stablecoins)
You’re going to require crypto ownership to take part in DeFi. You can begin by buying major digital coins like BT, ETC, or stablecoins. Stablecoins are pegged on the dollar and are meant to exchange at a rate of 1 dollar per coin. You will need a crypto exchange account to buy digital assets. We recommend Coinbase for beginners, although you’re free to go for any exchange that appeals to you. It’s user-friendly and secure.
Step 3 — CeFi or DeFi?
Now that you have bought crypto, you need to decide whether you will stick to Centralized exchanges or Decentralized exchange platforms. DeFi platforms are the best if you want to have the full experience of decentralized finance. While CeFi platforms are easy to use, and you don’t have to worry about your private keys, they have fewer features. You can’t stake or borrow in CeFi exchanges.
Step 4 — Get a Crypto Wallet
You would need a crypto wallet if you picked DeFi. Crypto wallets were developed to provide all DeFi functions under one roof. Non-custodial wallets are the most preferred by investors. They are more secure and hard to hack. Users have full control of access keys. Coinbase Wallet, MetaMask, and TrustWallet are among the most common crypto wallets.
Mitigating Risk: How to Protect Your Funds and Assets
DeFi is a fast-growing industry, but it’s important to remember that it’s also a high-risk space. As with any investment, there are risks associated with it, and it’s important to take measures to protect your funds and assets. Here are some ways to mitigate risk:
Understanding DeFi risk
Before investing, it’s important to understand the risks involved. The ecosystem is decentralized and largely unregulated. Thus, there is a higher degree of risk than with traditional finance. It’s important to understand the risks of each protocol and platform before investing.
Research protocols and platforms
To mitigate risk, it’s essential to do thorough research on the protocols and platforms being considered, before investing in them. This means reviewing whitepapers, researching the team behind the project, and looking at the protocol’s track record. An investor must look for audits, security reports, and any other information that can help them evaluate the security and stability of the platform.
Use secure wallets
Using a secure wallet is crucial when it comes to protecting the assets. Hardware wallets like Trezor and Ledger are the most secure, as they store the private keys offline. Software wallets like MetaMask and MyEtherWallet are also popular, but it’s important to keep them updated and secure to avoid hacks or theft.
Diversify your portfolio
Diversification is key to mitigating risk in any investment. By spreading the investments across multiple protocols and platforms, an investor can reduce the risk of losing all their funds if one project fails.
Monitor your investments
It’s important to keep a close eye on investments, as the space is constantly evolving. This implies regularly checking the portfolio and keeping up to date with the latest news and developments in the space.
Stay informed
Staying informed is crucial, as the space is constantly changing and evolving. An investor must follow reputable influencers, read industry news, and keep up with the latest trends and developments.
Use caution with high-risk investments
It offers a wide range of investment opportunities, but it’s important to approach high-risk investments with caution. Be sure to thoroughly research any high-risk investment before putting in any funds.
Seek professional advice
If an investor is new, or unsure about a particular investment, it’s always a good idea to seek professional advice. This could mean consulting with a financial advisor or seeking out the opinions of experienced investors in the space.
Keep your private keys safe
Protecting private keys is essential to securing the assets. One should never share their private keys with anyone, and consider using a hardware wallet for added security.
Consider insurance options
As the space grows, so does the availability of insurance options for investors. Some protocols offer insurance options for their users, while others partner with third-party insurance providers. An investor must consider adding insurance coverage to their portfolio to protect against unforeseen events.
What is DeFi DApps?
Decentralized Finance applications are decentralized applications built on blockchain technology that offer traditional financial services, such as lending, borrowing, trading, and investing, in a decentralized, trustless, and open manner. They use smart contracts and digital assets to eliminate intermediaries and enable peer-to-peer transactions, allowing users to access financial services without the need for a centralized authority.
Decentralized finance applications have significantly impacted the traditional financial system, offering users greater autonomy, control, and transparency over their financial assets. These applications provide an alternative to the traditional centralized financial system, which relies on intermediaries such as banks, brokers, and other financial institutions. These applications use blockchain technology, which is decentralized, transparent, and immutable, ensuring the security and integrity of transactions. By eliminating intermediaries, it also reduces costs, fees, and transaction times, making financial services more accessible to everyone, including those who are unbanked or underbanked. Furthermore, these DApps allow for new and innovative financial products and services to be created, such as yield farming, liquidity pools, and prediction markets. The significance of these applications in the ecosystem is evident from the rapid growth of the market, with billions of dollars locked in smart contracts and thousands of users participating in Decentralized Finance activities.
What makes a DeFi DApp: These are characterized by their decentralized architecture, open-source code, and the use of smart contracts. They rely on decentralized protocols and blockchain networks, allowing them to operate transparently and independently of a centralized authority. They use open-source code, which allows anyone to inspect and audit the code, ensuring transparency and security. The applications also use smart contracts, which are self-executing digital contracts that enforce the rules and conditions of a transaction.
Types of DeFi DApps:
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXes):
These are platforms for exchanging digital assets without the need for intermediaries. They allow users to trade assets in a peer-to-peer manner, without the need for a central authority or custodian. Some examples of decentralized exchanges (DEXes) include Uniswap, SushiSwap, Curve Finance, and PancakeSwap. These platforms use smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies and other digital assets. Users can earn rewards by providing liquidity to these exchanges, which can lead to a more efficient market for trading digital assets.
Lending and Borrowing DApps:
These are platforms that enable users to lend and borrow digital assets in a decentralized manner, without the need for intermediaries. They allow users to earn interest on their assets or borrow assets for a certain period of time.
One example of a lending and borrowing platform is Aave, which allows users to lend and borrow a wide range of digital assets, including stablecoins, cryptocurrencies, and tokens. Lenders on Aave can earn interest on their deposited assets, while borrowers can use the funds to take advantage of market opportunities or hedge against risks. Aave also offers a unique feature called flash loans, which allow users to borrow funds without any collateral, as long as the loan is paid back within the same transaction.
Derivative DApps:
Derivative DApps are another type of application that allows users to trade derivative contracts, such as futures and options, in a decentralized manner. These platforms use smart contracts to execute trades automatically, without the need for intermediaries. This allows users to access derivatives trading features without the traditional barriers to entry, such as high fees, complex requirements, and limited availability. Some examples of derivative DApps include Synthetix, dYdX, and Hegic. These platforms offer various types of derivative trading, such as synthetic assets, perpetual futures, and options. They provide users with a more accessible, efficient, and transparent way to trade derivatives, which is not possible through traditional financial systems.
Stablecoins DApps:
Stablecoin DApps are digital assets that provide price stability, and are designed to maintain a stable value, usually pegged to a fiat currency or a commodity. They offer a reliable store of value, which is not subject to the high volatility that is often associated with other cryptocurrencies. Stablecoins are used in many applications, including lending and borrowing, trading, and investing. They enable users to avoid the risks of price fluctuations and provide a more stable option for transacting on blockchain networks. Some popular examples of stablecoins are Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), Dai (DAI), and TrueUSD (TUSD). These stablecoins are widely used in applications and are considered an important part of the ecosystem.
Payment DApps:
Payment DApps enable users to make decentralized payments and transfers in a trustless and transparent manner. They leverage blockchain technology to eliminate the need for intermediaries, enabling users to transfer funds directly to each other. These DApps provide an alternative to traditional payment systems, which are often centralized and charge high fees. Payment DApps allow for fast, low-cost, and secure transfers of value, making them particularly useful for cross-border transactions. Some examples of Payment DApps include Request Network, OmiseGO, and Ripple.
Insurance DApps:
Insurance DApps are platforms that offer decentralized insurance services, allowing users to protect their digital assets against various risks. They use smart contracts to automate the underwriting and claims process, enabling a transparent and trustless system that removes the need for intermediaries. Insurance DApps offer different types of insurance products, such as coverage for smart-contract failures, asset theft, and price volatility. Users can purchase insurance policies using digital assets and receive payouts automatically if the insured event occurs. Examples of insurance DApps include Nexus Mutual, Etherisc, and InsurAce.
Wallet DApps:
Wallet DApps are decentralized crypto wallets that allow users to store and manage their digital assets in a secure and decentralized manner. They are usually non-custodial, so users retain control of their private keys and assets, without relying on a centralized authority. These wallets often support multiple cryptocurrencies and enable users to interact with various applications, such as DEXes, lending platforms, and payment systems, without leaving the wallet interface. Some popular wallet DApps include MetaMask, MyEtherWallet, Trust Wallet, and Coinbase Wallet.
Prediction Market DApps:
These are platforms that allow users to bet on the outcome of future events, using blockchain technology to ensure transparency and fairness. They allow users to buy and sell shares in the predicted outcome of events, such as elections or sports matches, and earn a profit if their prediction is correct. Some examples of prediction market DApps include Augur, Gnosis, and Polymarket.
Tokens:
Tokens are digital assets that represent value and can be traded on blockchain networks. In the DeFi ecosystem, there are several types of tokens, including:
Application Tokens:
Application tokens are a type of token that is designed to be used within a specific DApp. They are often used to grant users access to certain features or functionalities, such as discounted fees or exclusive content. For example, the COMP token is the native token of the Compound lending platform, and is used to vote on governance proposals and earn rewards for providing liquidity.
Governance Tokens:
Governance tokens are an important part of the ecosystem, as they allow users to have a say in the development and direction of a particular DApp. Examples of governance tokens include UNI for Uniswap, COMP for Compound, and MKR for MakerDAO. Holders of these tokens can vote on proposals for changes to the protocol, such as adding new features or modifying existing ones, and can also receive a portion of the fees generated by the platform. Governance tokens are often distributed to users through liquidity mining programs, where users provide liquidity to a particular DApp in exchange for tokens.
Transactional Tokens:
Transactional tokens are an important component of the blockchain ecosystem, as they allow users to perform transactions and execute smart contracts on a blockchain network. Some examples of transactional tokens include Ether (ETH) on the Ethereum network, Binance Coin (BNB) on the Binance Smart Chain, and Sol (SOL) on the Solana network. These tokens are used to pay for gas fees, which are required to execute a transaction on the network. By using these tokens, users can make transactions on the network in a decentralized, trustless, and transparent manner, without the need for intermediaries.
Security Tokens:
Security tokens are a type of digital asset that represents ownership of a real-world asset. These assets are backed by tangible assets, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or real estate. Security tokens are issued on a blockchain, which provides transparency, immutability, and security to the transactions. They allow for fractional ownership, which enables smaller investors to participate in investments that were previously reserved for larger investors. Security tokens also offer increased liquidity, as they can be traded on decentralized exchanges, allowing investors to easily buy and sell their assets. Examples of security token offerings (STOs) include Blockchain Capital, tZERO, and Harbor.

Tips for Using DeFi Applications
Decentralized Finance applications can offer exciting investment opportunities but can also come with risks. Here are some tips to keep in mind when using these applications:
Familiarize yourself
It is essential to understand what DeFi is and how it works before investing in any application. Familiarize yourself with the fundamental concepts, such as the use of smart contracts, blockchain technology, and decentralized architecture. This can help you make informed investment decisions.
Conduct thorough research
Before investing in any application, do your research to understand the project’s background, development team, and community. Look for reviews and opinions from other investors to get a sense of the project’s potential and any possible risks.
Use secure wallets
When interacting with applications, you will likely need to connect a digital wallet to the application. Ensure that you use a secure wallet that allows you to maintain control of your private keys. Avoid sharing your private keys with anyone or any application, as this can lead to the loss of your assets.
Diversify your portfolio
Diversification is essential in any investment strategy. Consider investing in a variety of applications and different types of products to spread your risk and increase your chances of returns.
Monitor your investments
Keep track of your investments to stay informed about their performance. Watch for any sudden drops or spikes in value, as these can be indicators of potential issues or opportunities.
Stay informed
The ecosystem is rapidly evolving, and new applications and products are regularly being introduced. Stay informed about new projects, their features, and their risks to ensure that you are making informed investment decisions.
Use caution with high-risk investments
Some applications may offer high-risk, high-reward investment opportunities. While these can be attractive, they can also lead to significant losses. Use caution when investing in high-risk applications, and only invest what you can afford to lose.
Seek professional advice
If you are new or unsure about a particular investment, seek professional advice from a financial advisor or investment professional. They can offer you valuable insights and help you make informed investment decisions.
Keep your private keys safe
Your private keys are the only way to access and manage your assets. Keep them safe by storing them in a secure wallet, or a hardware wallet stored in an offline location, and avoid sharing them with anyone.
Continuously educate yourself
The ecosystem is constantly evolving, and staying up-to-date with the latest developments can help you make informed investment decisions. Continuously educate yourself about new projects, products, and risks in the space.
DeFi in Gambling
Gambling is one of the most progressive industries. The internet became popular towards the end of 1991, and by 1994, the first online casino was launched. Ever since, the sector has continued to explore every new technology that comes up. DeFi is the new darling on the block, so gamblers couldn’t be left out. We are not just talking about land-based casinos. Covid 19 lockdowns forced casinos to seek alternatives online. Blockchain technology offers transparent and secure ways of betting. Many gambling providers started adopting cryptocurrencies, and today there is clear evidence that the future of casinos and sports betting is in DeFi.
There are several benefits of DeFi gambling. Let’s look at them.
- Transparency
Trust is the biggest issue in gambling. DeFi gambling is blockchain-based, so it’s transparent, and bettors have no illusions that they will be rigged out. Of course, the house may still win in the long run because that’s the nature of gambling. However, when players use DeFi or dApps, they are sure that all losses and wins are 100% genuine. Meaning participants can now enjoy a plethora of gambling options without worrying about losing their money to dishonest operators. This is because blockchain records everything immutably, including losses, wins, and payouts.
- Provably Fair Games
Another significant benefit of DeFi is the introduction of provably fair games. Nothing worries a gambler more than being cheated. Speculators are willing to take substantial stakes as long as they are sure there is fairness. Provably fair games are a surefire way of proving fairness in gambling. They remove third parties and introduce a fairness verification system between casino operators and bettors. The fairness verification system is irrevocable and undisputable. For example, after playing a given spin in a slot machine, you can key in seed numbers into a hashing tool to find out whether the casino tampered with the outcome or not.
- DeFi Games
DeFi games are hosted and played on the blockchain. What’s most attractive about them is that they offer players numerous rewards to players. You can earn real money by taking part in DeFi games. There’s nothing better than making money while being entertained. That’s why play-to-earn games have become so popular.
- Metaverse Casinos
The metaverse is a futuristic immersive virtual world. Members can buy land, own houses, operate shops and even play games. It works like the real world. All you need is an avatar that represents you to get started. Casinos have already begun creeping into the metaverse as they seek to provide immersive betting environments to their clients. Metaverse casinos rely on smart contracts and cryptocurrencies to implement their functions.
DeFi Financial Products
Uniswap: Token exchange

UniSwap is one of the oldest and largest decentralized exchanges. Its Native and governance token is UNI. The platform uses a permissionless model allowing accessibility to anodyne over the internet with zero restrictions. It’s 100% governed by smart contracts and lets users trade all major tokens from the wallet. It supports more than 1800 tokens and 2000 coins. As the name indicates, UniSwap doesn’t accept fiat transactions. It’s a crypto-to-crypto trading platform. If you’re just getting started, buy BTC, ETH, or a coin of your preference from a fiat compatible exchange and send it to your UniSwap wallet. UniSwap enables peer-to-peer market making. It runs on the Ethereum blockchain network, which uses the proof-of-work operating model. As a UniSwap DeFi user, you can create new markets with smart contracts, use current markets to swap digital coins, stake to earn rewards, or participate in voting through UNI tokens.
Augur: Market prediction platform

Augur is a trustless DeFi platform for market prediction. Users can stake in the outcome of a real-world event. Like betting or binary options, users place bets and earn rewards when they win. The less likely the event, the higher the premium. More likely, events have fewer rewards. It offers several markets, including non-finance-related options such as gossip and even weather updates. For example, you can bet on a question like, “Will Donald Trump regain his Twitter account on 5th July 2022?” Your bet, in this case, is a simple yes or no. You’ll come across three main types of predictions, yes/no, multiple-choice, and scalar ( predictions with lower and upper bands). The platform founders believe that Augur will help tap into the crowd’s wisdom to spread quick and easy-to-read information in every sector. Augur is built on Ethereum. Its native token REP is used to place bets and participate in Augur competitions.
PoolTogether: Zero loss savings platform

Not everyone who participates in a lottery wins. But what if there were no losers? This is what DeFi service provider PoolTogether offers. It allows users to stake crypto into a lottery programmer for a chance to win attractive weekly and monthly prizes. There is a weekly or monthly winner but no losers. Yes, there are absolutely no losers because everyone else who didn’t win gets back their initial investment at the end of the bet. So your only cost will be trading fees, but you don’t lose your money. It’s an Ethereum-based platform that describes itself as “prize savings,” meaning you get rewarded for saving. Instead of holding your crypto elsewhere, you could keep it and bet with it at PoolTogether since there are no risks, yet if you win the draw, you could potentially take home a huge price. The best part is that there are no lengthy account opening procedures. Simply go to the PoolTogether website, connect to your Web3 wallet, and get started.
Compound: Borrow and lend

Compound is a sophisticated blockchain-built borrowing and lending app that’s the DeFi version of what we call money markets in traditional finance. The protocol allows users to borrow and lend in crypto, just like you can take loans from a bank or save to earn interest. Supported cryptos include Ether, Tether, USD Coin, Augur, Wrapped BTC, Dai, Basic Attention Token, True USD, Sai, Sushi Token, Oz, Maker, Uniswap, ChainLink Token, Aave Token, and Yearn Finance. Lenders stake their crypto into different liquidity pools to earn dynamic interest rates annually. Interest is paid to lenders in the same crypto-token they use to stake. Like banks, Compound loans are secured by the crypto savings balance of a borrower. So you must open an account and start saving to qualify for a loan. DeFi is anonymous, and there are no credit score checks, so borrowers qualify for a percentage of their savings according to several determining factors. Loans are paid with compound interest rather than a fixed rate. So the cost of borrowing keeps varying with your loan balance. Keep in mind that Compound itself doesn’t offer loans but instead matches lenders and borrowers in a peer-to-peer fashion.
MakerDAO: Decentralized reserve bank and stablecoin

Maker is stablecoin and lending DeFi lending project. However, the concept is very different from lending dApps like Compound in that it is like a central bank but decentralized. It’s an Ethereum-based project governed by MakerDAO through Maker token (MKR) and uses DAI for transactions. These are its two native coins. DAI is a USD-pegged stablecoin backed by crypto collateral from user deposits and is kept stable by MKR. Maker strives to operate pretty much like the Fed without breaking the founding tenets of DeFi. Holders of DAI can even vote just like the Fed community votes on interest rates. Holders of MKR can take collateralized loans in DAI stable coin, with MKR as the security. The borrower’s collateral is automatically sold when they fail to repay their loans accordingly. Everything is governed by Ethereum protocol smart contracts.
DeFi Currency
There is no single currency that works best in DeFi. The ecosystem is designed to work with cryptocurrencies. DeFi products work with a variety of cryptos, from major ones to tokens.
Tokens are so far the most actively used currencies as most platforms have their own native coins. The technology is, however, still new, so it’s not possible to determine which coins will dominate in the future. The common denominator is that all DeFi currencies are compatible with smart contracts.
While the entire crypto sector is currently valued at over $1.5 trillion, DeFi native tokens make up about $124 billion in market cap, slightly less than 10% of the entire digital coins market cap. Most DeFi platforms are DAOs, meaning they are governed by their members through a democratic voting system, in which case, the ecosystems’ native tokens give holders special voting rights. Users with more tokens have more voting rights based on the assumption that a member’s interest in the success of a project can be measured by how much they are willing to invest in it. Uniswap is so far the largest native token with governance rights. It had a fully diluted market cap of $5.3 billion as of writing this.
The Future of DeFi
DeFi’s future looks bright. We can call it the innovation of the century. The technology behind it offers solutions to many problems of traditional finance. Just like the wealth management space is being disrupted by artificial intelligence, DeFi is the next significant disruption in the banking sector. And we are not talking just about finance. DeFi is finding use cases in governance, transport, entertainment, energy, and even in the health sector.
That said, the journey will not be without hurdles. Government regulations are the main challenges that lie ahead. Regulators are hardly up to speed with technology. This could mean the introduction of unfavorable, poorly structured laws, especially for the smart contract sector that feels it doesn’t need regulation. The ongoing lawsuit between SEC and XRP is a perfect example of regulatory problems that emerging technologies encounter. In the end, technology always wins, so DeFi is here to stay and lead us to a future of integrated value exchange.
Conclusion
DeFi is a new experience with a world of possibilities. It’s not just different from traditional finance but is also exciting. Although it’s still in its infancy days, participants are already reaping huge rewards. From provably fair gambling to earning massive returns from yield farms to individuals taking loans on the blockchain. The potential that DeFi carries can’t be ignored. The best part is that it’s permissionless, so anyone can join without restrictions. Simply get a Web3 or DeFi wallet to get started. If you’re interested in staking, a rule of the thumb is to invest your risk capital only. Cryptocurrencies are volatile, and they can lose value at any time.
What is DeFi and how does it work?
What is DeFi and how does it work?
Decentralized Finance (also known as DeFi) is a form of blockchain-based finance that doesn’t rely on a central financial intermediary like an exchange, brokerages, or banks to offer traditional financial instruments. Rather, DeFi relies on smart contracts on blockchains like Ethereum and therefore massively improves traditional finance.
Through DLT Users can access financial products directly on the blockchain, without the need for any middlemen like banks. In other words, users can trade crypto currencies, acquire insurances, borrow or lend funds, invest in different assets using derivatives and NFTs and earn interest in saving accounts through DeFi platforms.
DeFi democratizes finance and brings financial opportunities to the unbanked and underbanked. DeFi connects users directly via blockchain technology, commonly known as the DeFi protocol, creating a peer to peer financial network. Its products and smart contracts ensure that all agreements are fulfilled and therefore eliminate the need for intermediaries.
1.Is Bitcoin a Decentralized Finance?
1.Is Bitcoin a Decentralized Finance?
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency running on a decentralized Blockchain. DeFi doesn’t refer to any specific coin but rather the entire concept of a financial system built on a decentralized distributed blockchain like the technology behind Bitcoin and Ethereum. DeFi enables users to borrow, lend and even trade. Bitcoin is simply a store of value, so it’s not decentralized finance.
2. What Is Total Value Locked in DeFi?
2. What Is Total Value Locked in DeFi?
Total Value Locked (TVL) in DeFi is simply the total amount of staked or invested cryptocurrency earning rewards.
3. Who created DeFi?
3. Who created DeFi?
No one created DeFi. Neither is owned by any single person. It’s a concept that was inspired by Bitcoin but built on smart contract blockchains like the Ethereum network. It’s programmable, so anyone with coding skills can take part in developing DeFi.
What is liquidity provision and how does it work?
What is liquidity provision and how does it work?
Liquidity provision refers to the act of providing liquidity to a protocol in exchange for rewards, such as fees or governance tokens. Liquidity providers typically deposit equal amounts of two different assets into a liquidity pool, which is then used to facilitate trades between those assets on the platform. In exchange for providing liquidity, providers receive a portion of the fees generated by the platform, as well as a share of the governance tokens.
How do I find the best DeFi opportunities and stay informed about DeFi news and developments?
How do I find the best DeFi opportunities and stay informed about DeFi news and developments?
There are a number of ways to stay informed about news and developments, including following key influencers and projects on social media, joining specific forums and discussion groups, and subscribing to newsletters and blogs. In terms of finding the best opportunities, it’s important to conduct thorough research, stay up to date on news and trends in the space, and consult with trusted advisors when making investment decisions.
Can I make a profit with DeFi and how do I measure its performance?
Can I make a profit with DeFi and how do I measure its performance?
Yes, it is possible to make a profit, but as with any investment, it comes with risks. To measure the performance of your investments, you can track the price of the cryptocurrency assets you’ve invested in, as well as monitor any rewards you may be earning through staking or liquidity provision. It’s also important to track the TVL, and user adoption of the applications you’ve invested in, as these metrics can provide valuable insights into the potential long-term success of a given project.
How is DeFi regulated and what are the legal considerations?
How is DeFi regulated and what are the legal considerations?
It is a relatively new and rapidly evolving space, and as such, there is currently no clear regulatory framework in place. Some projects are attempting to navigate existing regulatory structures, while others are seeking to create new decentralized governance models that are independent of traditional regulatory structures. It’s important to be aware of the legal considerations and potential risks associated with investing in projects, and to consult with legal and financial advisors when making investment decisions.